 |
| Image Source: https://goo.gl/r2miTF |
Summary:
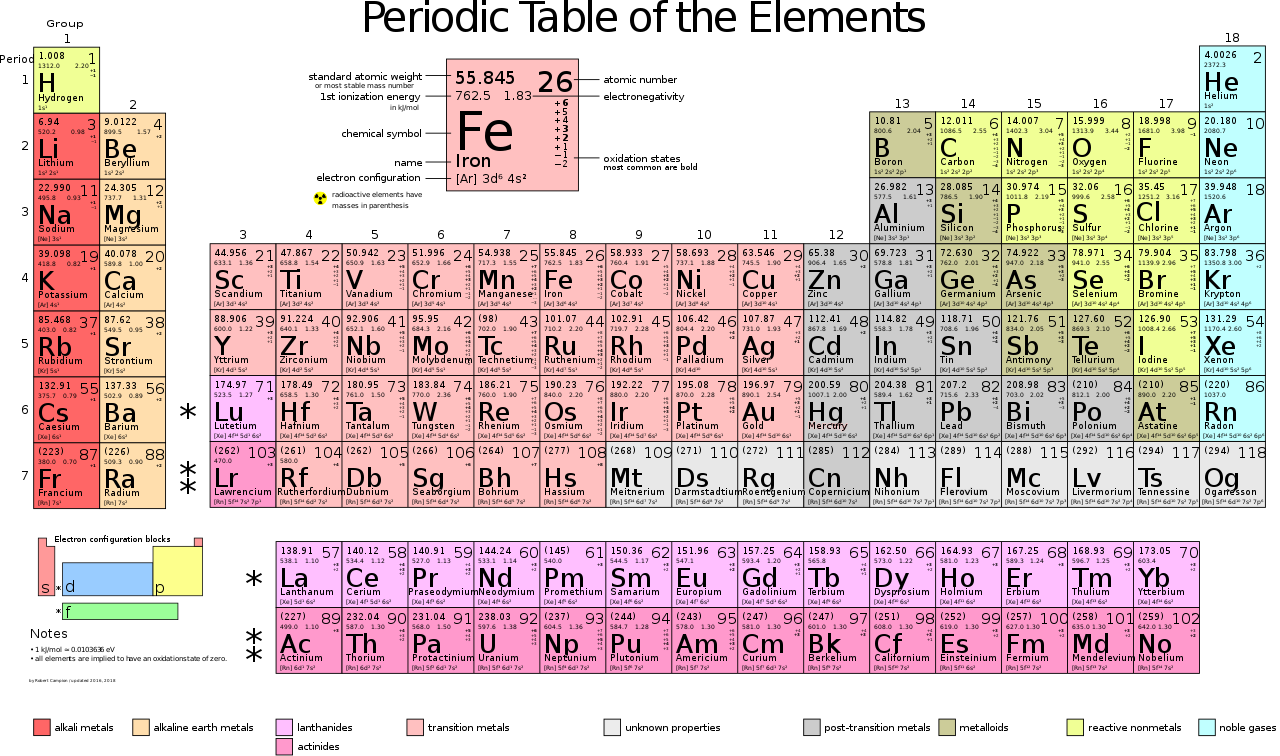
The periodic table is a table that organizes all 118 elements on earth from left to right. based on their atomic number. Each column is called a family and each row is called a period. Each element in a period has the same energy levels, and as you go down, there is an extra energy level added. An energy level is an imaginary circle around the nucleus of an atom. The first energy level contains a maximum of two atoms and the second energy level contains a maximum of 8 atoms. The further the energy level, the higher the electron capacity in that energy level. In the periodic table, there are five families: The alkaline metals, the Alkaline Earth Metals, the Transition Metals, the Boron Family, Carbon Family, Nitrogen Family, Oxygen Family, Halogens, and Noble Gases. Noble Gases don't react at all while Halogens and Alkaline Metals are very reactive. Transition Metals and Alkaline Earth Metals mold and bond with another atom.
SP5 - Using Mathematics:
This week, I performed mathematics to find how many protons, electrons, and neutrons were in the first 20 elements of the periodic table. The only thing provided was the element name, number and mass. To find the amount of protons and electrons, I simply looked at the atomic number since the the atomic number shows the amount of protons and a balanced atom would have the same number of atoms and electrons. To find the amount of neutrons, I subtracted the atomic mass by the amount of protons, since the atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons. Then I rounded to make the amount of neutrons a whole number, since you cannot have a part of a neutron.
XCC - System and System Models:
One system (not necessarily a system) was the atom. The atom is the most basic building block of matter. There are three parts that make up an atom- the electron (negative charge), the proton (positive charge) and the neutron (neutral charge). The electrons and the protons determine the charge of the atom. If there as an unstable charge (an uneven amount of protons and electrons), the atom won't be able to function. The neutron determines the stability of the atom. There can be an extra amount of protons and these are called isotopes. However, if there are too many protons, the atom may become unstable and not work. This system of atoms can be connected to another system of atoms to create bigger things such as cells which can create organisms.


